Advantages:
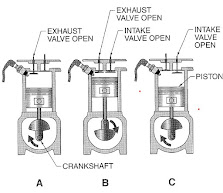
1) The two-stroke cycle engine gives one working stroke for each revolution of the
crankshaft. Hence theoretically the power developed for the same engine speed and
cylinder volume is twice that of the four-stroke cycle engine, which gives only one
working stroke for every two revolutions of the crankshaft. However, in practice,
because of poor scavenging, only 50-60% extra power is developed.
2) Due to one working stroke for each revolution of the crankshaft, the turning moment on
the crankshaft is more uniform. Therefore, a two-stroke engine requires a lighter
flywheel. 3) The two-stroke engine is simpler in construction. The design of its ports is much
simpler and their maintenance easier than that of the valve mechanism.
4) The power required to overcome the frictional resistance of the suction and exhaust strokes
is saved, resulting in some economy of fuel.
5) Owing to the absence of the cam, camshaft, rockers, etc. of the valve mechanism, the
mechanical efficiency is higher.
6) The two-stroke engine gives fewer oscillations.
7) For the same power, a two-stroke engine is more compact and requires less space than a
four-stroke cycle engine. This makes it more suitable for use in small machines and
motorcycles.
8) A two-stroke engine is lighter in weight for the same power and speed especially when
the crankcase compression is used.
9) Due to its simpler design, it requires fewer spare parts.
10) A two-stroke cycle engine can be easily reversed if it is of the valveless type.
Disadvantages:
1) The scavenging is not very efficient in a two-stroke engine, the dilution of the
charges takes place which results in poor thermal efficiency.
2) The two-stroke spark-ignition engines do not have a separate lubrication system and
normally, lubricating oil is mixed with the fuel. This is not as effective as the
lubrication of a four-stroke engine. Therefore, the parts of the two-stroke engine are
subjected to greater wear and tear.
3) In a spark-ignition two-stroke engine, some of the fuel passes directly to the exhaust.
Hence, the fuel consumption per horsepower is comparatively higher.
4) With heavy loads a two-stroke engine gets heated up due to the excessive heat produced. At the same time, the running of the engine is riot very smooth at light loads.
5) It consumes more lubricating oil because of the greater amount of heat generated.
6) Since the ports remain open during the upward stroke, the actual compression starts
only after both the inlet and exhaust ports have been closed. Hence, the compression
ratio of this engine is lower than that of a four-stroke engine of the same dimensions.
As the efficiency of an engine is directly proportional to its compression ratio, the efficiency of a two-stroke cycle engine is lower than that of a four-stroke cycle engine
of the same size.












:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Fuelinjector-5c2ce49a46e0fb00014ac030.png)










